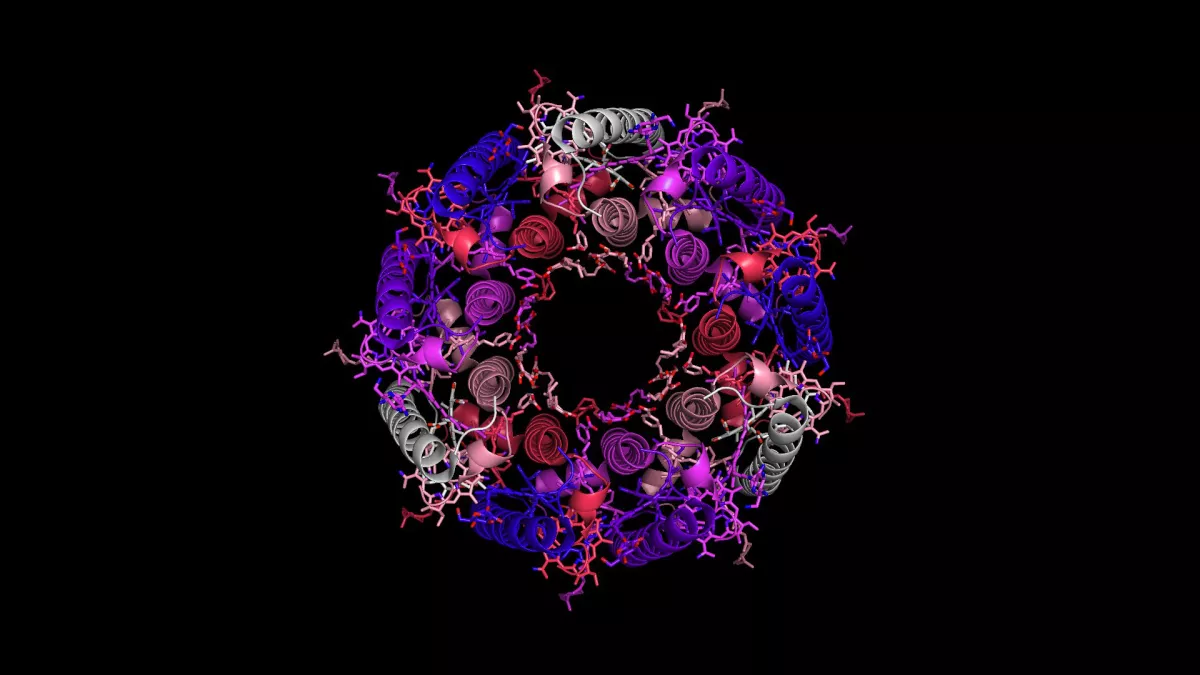
Sub-atomic hardware, similar to this light-gathering complex from a bacterium, is frequently strikingly even.
Sub-atomic hardware, similar to this light-collecting complex from a bacterium, is frequently strikingly even. (Picture credit: Iain Johnston)
In science, balance is regularly the standard as opposed to the exemption. Our bodies have left and right parts, starfish transmit from an essential issue and even trees, however not generally balanced, still produce balanced blossoms. Unevenness in science appears to be very uncommon by examination, as a matter of fact.
Does this imply that development has an inclination for balance? In another review, a global gathering of specialists, drove by Iain Johnston, a teacher in the Division of Science at the College of Bergen in Norway, says it does.
Albeit balanced structures address just a little part of potential structures — in calculation, at any rate — evenness springs up wherever in residing living beings. It’s not only a body-plan peculiarity, by the same token. Proteins, the sub-atomic hardware inside a body, are generally balanced too, frequently being made out of a progression of rehashing, secluded parts. Rehashing structures are in many cases found in creatures, as well; consider centipedes, with their rehashing body portions. The justification for this evident “inclination” isn’t driven by feel. All things considered, as per the specialists, it comes down to effortlessness.
Supported Connections
Undoubtedly! The World’s Best Breakfast
Kachava
“It very well may be enticing to expect that evenness and seclusion emerge from regular choice,” Johnston and his co-creators wrote in the new review. Regular choice can make gainful qualities become more normal since those characteristics help endurance. Be that as it may, regular choice can make a useful quality more normal or get rid of a destructive one; it can’t compel spic and span ones to show up.
All things being equal, it can support the impacts of changes that happen arbitrarily. For instance, moths with dull shaded wings may be more diligently so that birds might be able to see than moths with light-hued wings. Hunters could accordingly be bound to neglect dull winged moths, empowering a greater amount of those bugs to get by, imitate, and give that characteristic to their posterity. In any case, this doesn’t compel dark wings into reality; a quality needs to change for that to occur. Furthermore, on the off chance that a transformation gives a benefit, it’s bound to be propagated among a populace for ages, until it turns into a typical quality for the species.
Related: Qualities of 500-million-year-old ocean beasts live inside us
Similarly, regular choice could appear to lean toward evenness since it is generally given balanced structures to work with. The most probable clarification for why proteins and bodies are even isn’t on the grounds that balance gives an endurance advantage, but since more balanced, rehashing structures show up in any case.
So what gets that going? Balanced structures have likely developed all the more habitually and afterward persevered throughout transformative time since they frequently require less data to deliver than awry structures do.
“Envision advising a companion how to tile a story utilizing as couple of words as could be expected,” Johnston said in an explanation. “You wouldn’t agree, ‘Put precious stones here, long square shapes here, wide square shapes here.’ You’d express something like, ‘Put square tiles all over.’ And that straightforward, simple recipe gives a profoundly symmetric result.”
Johnston and his associates tried this straightforwardness speculation by utilizing computational demonstrating. By running a reproduction of protein development, the scientists observed that irregular changes are significantly more prone to deliver straightforward hereditary successions than complex ones. In the event that those basic designs are sufficient to go about their responsibilities, regular determination can then dominate and utilize those designs. In the analysts’ reenactments, as well as throughout everyday life, high-evenness structures with low intricacy far dwarfed complex designs with low balance.
RELATED STORIES
—What is Darwin’s Hypothesis of Advancement?
—For what reason do Cambrian animals look so unusual?
—Top 10 things that make people extraordinary
The review reframes the supposed boundless monkey hypothesis, an old psychological study in the field of developmental science. If, as the hypothesis predicts, a monkey types haphazardly for a limitless measure of time, it will ultimately deliver the total works of Shakespeare (or maybe the content for “Die Hard”). Basically, irregular changes in DNA resemble composing monkeys. Given sufficient opportunity (and enough monkeys), it is a sureness that a few pretty brilliant changes will show up.
Yet, when a speculative monkey delivers Shakespeare’s whole index of work, the innovative animal will have likely currently composed an enormous number of short sonnets. Essentially, in the event that science is completely dependent on hereditary guidelines produced aimlessly (similar as crafted by a haphazardly composing monkey), it will create an extremely enormous number of basic guidelines, since those will show up considerably more regularly than complex bearings do. All things considered, intricacy is pointless when a straightforward arrangement is free, concentrate on creators closed.
In this way, the following time you stop to respect a blossom’s spiral evenness, you can likewise respect the proficiency of the more limited, less complex quality groupings that encoded for that characteristic.